Difference between Assembler, Compiler and Interpreter
Assembler
Defination: Assembler (computing), a computer program which translates assembly language to an object file or machine language format.
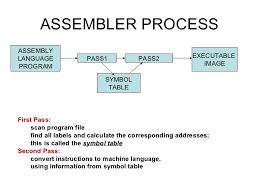
1. It translates the mnemonic codes such as PRN, ADD and SUB etc. to machine language code. It translates the high-level language to assembly language.
2. The program, which executes using assembler, executes faster because it directly converts the source code in machine language.
Read More: Algorithm And Pseudocode In C language With Example
Compiler
Defination: A compiler is a computer program (or a set of programs) that transforms source code written in a programming language (the source language) into another computer language (the target language), with the latter often having a binary form known as object code.
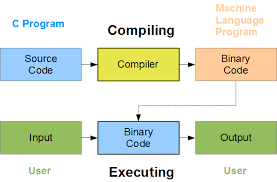
1.It translates the high-level language to assembly language.
2.It takes the time to execute a program because it first translates the source code into another compiler’s
language and then using assembler converts it into machine language.
Difference between Compiler And Interpreter
Compiler
Defination: A compiler is a computer program (or a set of programs) that transforms source code written in a programming language (the source language) into another computer language (the target language), with the latter often having a binary form known as object code.
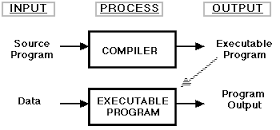
1. Compiler translates the entire high-level language program into the machine language program at one before executing it. This optimises the use of machine language instructions in the translated program.
Therefore normally compiled programs run faster than Interpreted programs. The original high-level language program is called as source program. The compiled program i.e. machine language program generated by the compiler after translation is called object program.